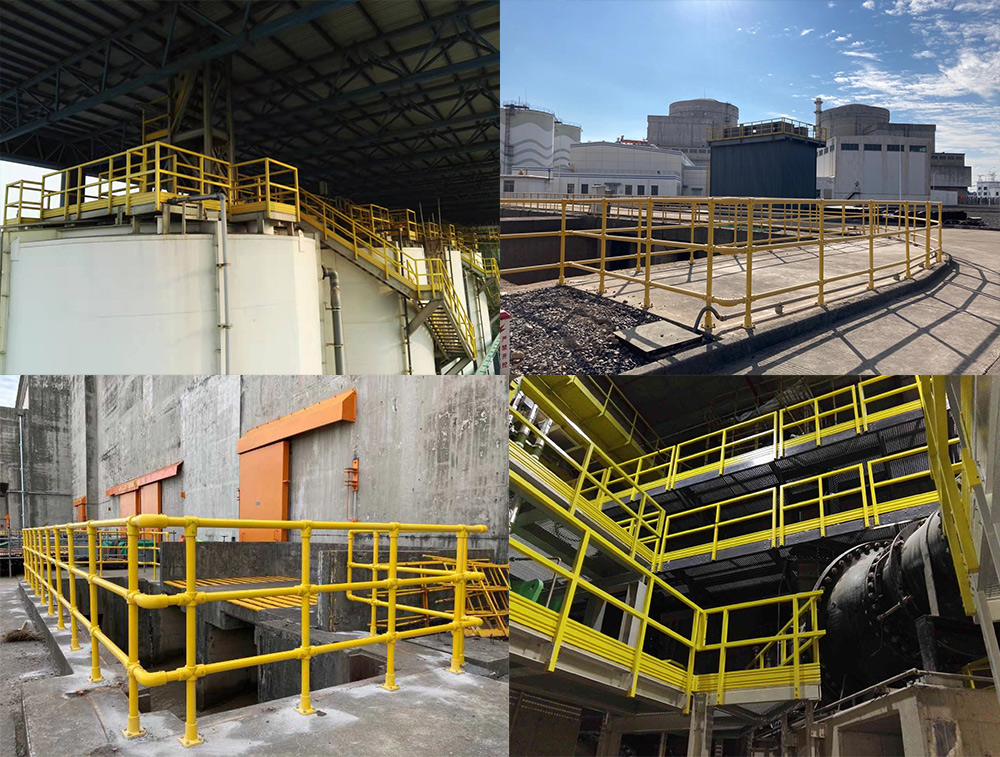
FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) handrail products are commonly used in various industries for safety and structural applications. These handrails are known for their durability, corrosion resistance, and low maintenance. FRP handrails are often preferred over traditional materials like steel or wood in environments where corrosion is a concern, such as chemical plants, offshore platforms, and coastal areas.

Key features of FRP handrail products may include:
Corrosion Resistance: FRP is resistant to corrosion caused by chemicals, saltwater, and other harsh environmental conditions.
Durability: FRP handrails are known for their long lifespan and ability to withstand heavy usage.
Lightweight: FRP is lighter than traditional materials, making installation easier and reducing the overall weight of structures.
Low Maintenance: FRP handrails generally require minimal maintenance, saving on time and costs over their lifespan.
Non-Conductive: FRP is a non-conductive material, making FRP handrails suitable for use in electrical environments where conductivity is a concern.
UV Resistance: FRP materials often have UV-resistant properties, making them suitable for outdoor applications.
Customization: FRP handrails can be designed and manufactured to meet specific project requirements, including size, shape, and color.
FRP Handrail&Railing Components
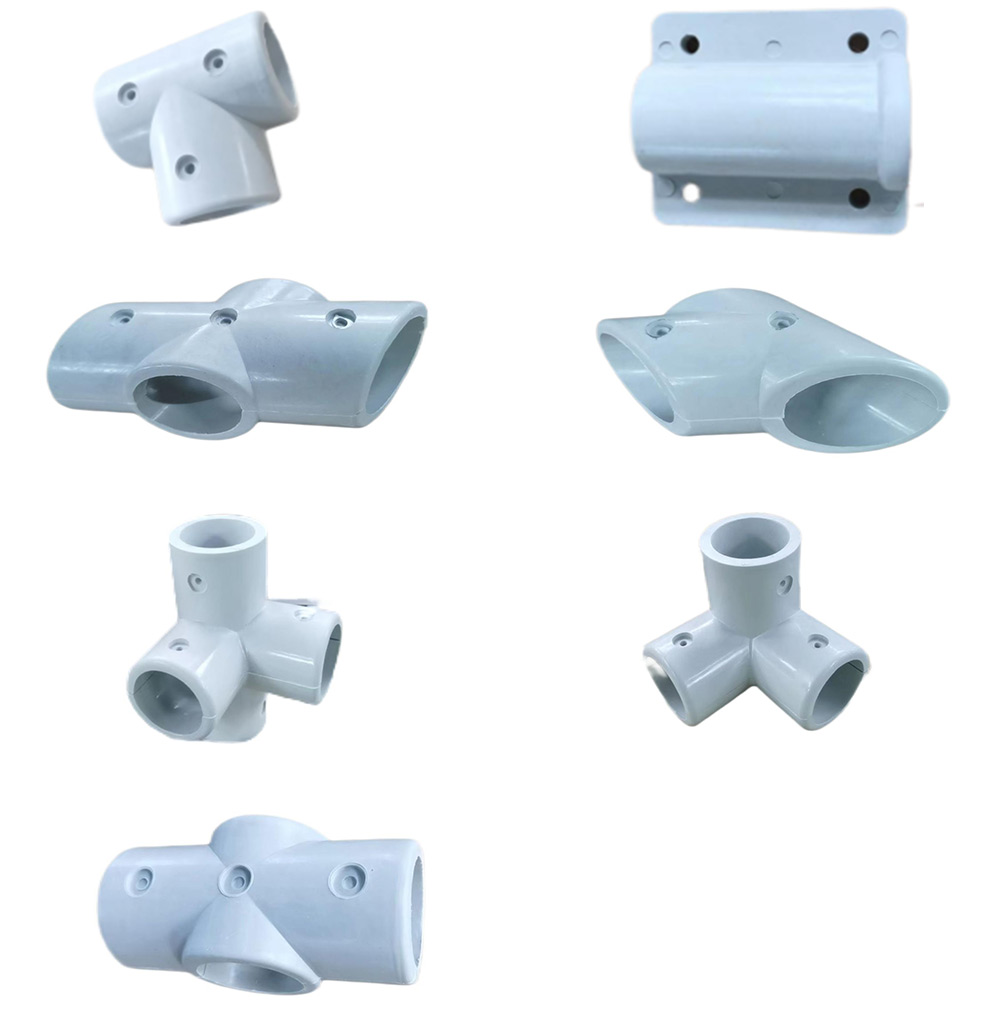

FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) handrail systems typically consist of various components designed to provide a safe and durable railing solution. The specific components may vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended use, but common elements include:
Rails: The horizontal components that users can hold onto for support. FRP handrail rails are designed to be sturdy and resistant to environmental factors.
Posts: Vertical supports that anchor the handrail system to the structure. Posts are important for the overall stability and strength of the handrail.
Connectors: These are fittings that join different sections of the handrail, including corners, angles, and straight runs. Connectors ensure a secure and rigid structure.
Base Flanges: The base flanges are used to secure the handrail system to the ground or structure. They provide stability and support to the posts.
Top Caps: Top caps cover the upper surface of the handrail, providing a finished appearance and preventing water from accumulating on the rail.
Mid-Rails: In some systems, a mid-rail is included between the top rail and the bottom rail for added safety. This provides additional support and helps prevent the passage of large objects between the rails.
Toe Plates or Kick Plates: These are optional components that can be added to the bottom of the handrail system to prevent objects from rolling or falling through the bottom.
Fasteners: Bolts, nuts, and other fasteners are used to securely attach various components together. Stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant fasteners are often preferred.
End Caps: End caps are used to finish the ends of the handrail and prevent any sharp edges from being exposed.
Accessories: Depending on the specific application, additional accessories such as gates, ramps, and custom fittings may be available to meet project requirements.
It's important to note that FRP handrail components are chosen and assembled based on the specific needs of the project, including factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, and safety regulations. Consulting with the manufacturer or supplier is recommended to ensure that the chosen components meet the necessary standards and specifications for the intended application.
When considering FRP handrail products, it's essential to ensure that they meet relevant safety standards and regulations for the specific industry or application. Additionally, consulting with a reputable manufacturer or supplier can help in choosing the right type of FRP handrail for a particular project.